Creating & Sharing Resources
When users create documents or other resources in Osvauld, they become the cryptographic owner with full control over access permissions. The system uses a combination of symmetric encryption for data protection and UCAN tokens for access control.
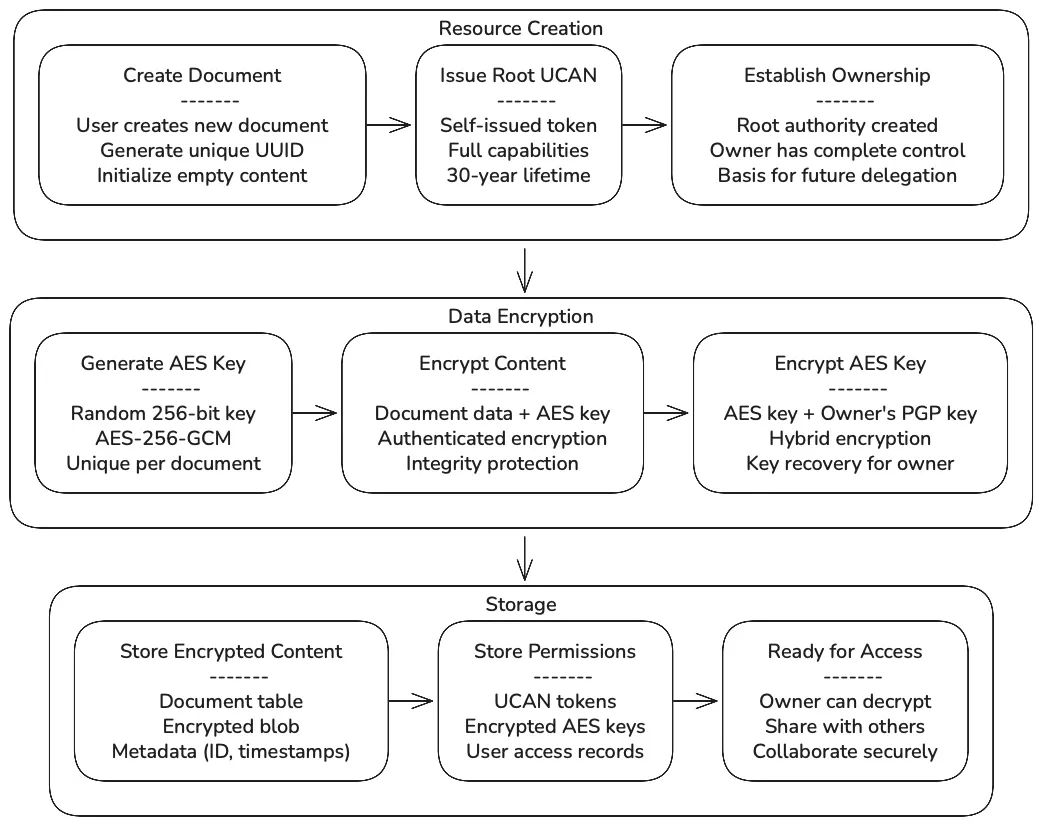
Resource Creation Process
Section titled “Resource Creation Process”Root Authority Establishment
Section titled “Root Authority Establishment”When a user creates a new document, they automatically become the root authority with a self-issued UCAN token:
{ "alg": "EdDSA", "typ": "JWT"}{ "aud": "alice_did", "cap": { "livnote:resource:document_uuid": { "crud/delete": [{}], "crud/read": [{}], "crud/update": [{}], "ucan/share": [{}] } }, "exp": 2702046575, "iss": "alice_did", "ucv": "0.10.0-canary"}Key properties of the root token:
- Self-Issued: Issuer and audience are identical (
alice_did) - Full Capabilities: All CRUD operations plus sharing rights
- Long Lifetime: 30-year validity period
- Resource-Specific: Tied to the specific document UUID
- Root of Trust: No proof field needed as this establishes authority
Data Encryption
Section titled “Data Encryption”The document content uses hybrid encryption:
- Generate AES Key: Random 256-bit AES-GCM key for the document
- Encrypt Content: Document data encrypted with AES key
- Encrypt AES Key: AES key encrypted with owner’s PGP public key
- Store Separately: Encrypted content and encrypted key stored as separate records
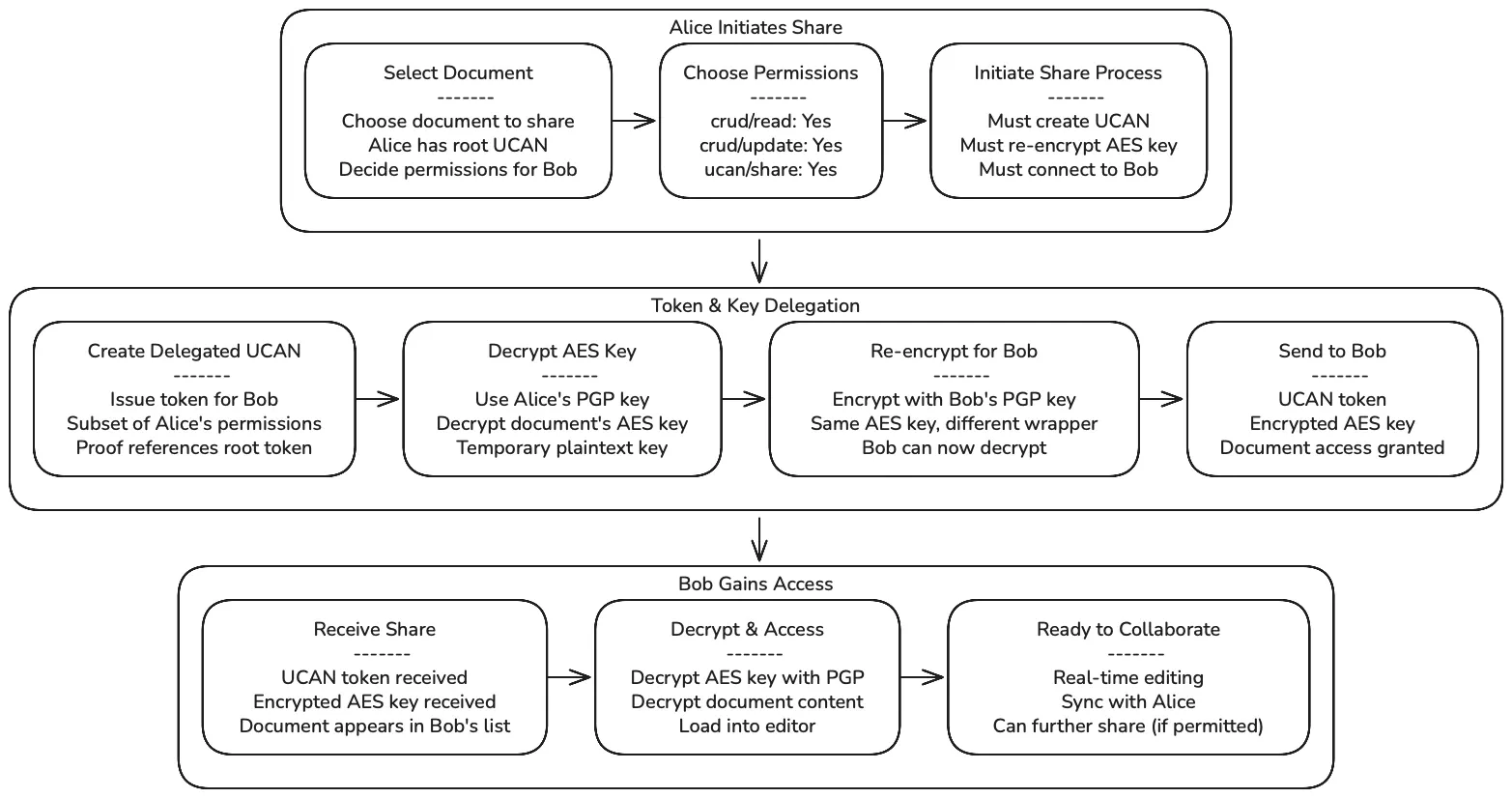
Resource Sharing Process
Section titled “Resource Sharing Process”Delegated UCAN Creation
Section titled “Delegated UCAN Creation”When Alice shares a document with Bob, she creates a delegated UCAN token:
{ "alg": "EdDSA", "typ": "JWT"}{ "aud": "bob_did", "cap": { "livnote:resource:document_uuid": { "crud/read": [{}], "crud/update": [{}], "ucan/share": [{}] } }, "exp": 2702046588, "iss": "alice_did", "prf": ["root_token_cid"], "ucv": "0.10.0-canary"}Key properties of the delegated token:
- Specific Audience: Targeted to Bob’s DID
- Subset of Capabilities: Alice can grant fewer permissions than she has
- Proof Reference: CID pointing to Alice’s root token
- Same Lifetime: Long-term access matching root token
- Delegation Chain: Links back to root authority
AES Key Re-encryption
Section titled “AES Key Re-encryption”Along with the UCAN token, Alice must provide Bob access to the encrypted data:
- Decrypt AES Key: Alice decrypts the document’s AES key using her PGP private key
- Re-encrypt for Bob: Encrypt the same AES key with Bob’s PGP public key
- Store Access Record: Save Bob’s UCAN token and encrypted AES key
- Enable Collaboration: Bob can now decrypt and collaborate on the document
Permission Validation During Sync
Section titled “Permission Validation During Sync”When Bob and Alice collaborate on the shared document, each CRDT operation requires permission validation:
- Present UCAN: Bob sends his delegated UCAN token with edit operations
- Validate Structure: Alice verifies token format and signature
- Check Audience: Confirms token is intended for Bob’s DID
- Validate Proof Chain: Resolves proof CID and validates back to root token
- Check Capabilities: Ensures Bob has required permission (e.g.,
crud/update) - Apply Operation: If valid, accept the CRDT operation
Transitive Sharing
Section titled “Transitive Sharing”When Bob (with ucan/share permission) wants to share the document with Carol:
- Bob creates delegated UCAN for Carol using his token as proof
- Re-encrypts AES key for Carol’s PGP public key
- Carol’s token contains proof chain: Bob’s token → Alice’s root token
- Validation requires full chain: Carol → Bob → Alice verification
Key Security Properties
Section titled “Key Security Properties”Cryptographic Ownership: Root UCAN establishes mathematical ownership, not just database records
Granular Permissions: Each capability can be granted or withheld independently
Proof Chain Integrity: Delegation chains provide cryptographic audit trail back to root authority
Data Confidentiality: AES encryption ensures only authorized users can decrypt content
Key Separation: UCAN tokens control access rights while AES keys control data decryption
Revocation Capability: Future implementation can revoke access by invalidating UCAN chains
This architecture ensures that resource sharing maintains both cryptographic security and fine-grained access control while enabling real-time collaboration between authorized users.